Hyperelasticity#
Author: Jørgen S. Dokken and Garth N. Wells
This section shows how to solve the hyperelasticity problem for deformation of a beam.
We will also show how to create a constant boundary condition for a vector function space.
We start by importing DOLFINx and some additional dependencies.
Then, we create a slender cantilever consisting of hexahedral elements and create the function space V for our unknown.
from dolfinx import log, default_scalar_type
from dolfinx.fem.petsc import NonlinearProblem
import pyvista
import numpy as np
import ufl
from mpi4py import MPI
from dolfinx import fem, mesh, plot
L = 20.0
domain = mesh.create_box(
MPI.COMM_WORLD, [[0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [L, 1, 1]], [20, 5, 5], mesh.CellType.hexahedron
)
V = fem.functionspace(domain, ("Lagrange", 2, (domain.geometry.dim,)))
We create two python functions for determining the facets to apply boundary conditions to
def left(x):
return np.isclose(x[0], 0)
def right(x):
return np.isclose(x[0], L)
fdim = domain.topology.dim - 1
left_facets = mesh.locate_entities_boundary(domain, fdim, left)
right_facets = mesh.locate_entities_boundary(domain, fdim, right)
Next, we create a marker based on these two functions
Concatenate and sort the arrays based on facet indices. Left facets marked with 1, right facets with two
marked_facets = np.hstack([left_facets, right_facets])
marked_values = np.hstack([np.full_like(left_facets, 1), np.full_like(right_facets, 2)])
sorted_facets = np.argsort(marked_facets)
facet_tag = mesh.meshtags(
domain, fdim, marked_facets[sorted_facets], marked_values[sorted_facets]
)
We then create a function for supplying the boundary condition on the left side, which is fixed.
u_bc = np.array((0,) * domain.geometry.dim, dtype=default_scalar_type)
To apply the boundary condition, we identity the dofs located on the facets marked by the MeshTag.
left_dofs = fem.locate_dofs_topological(V, facet_tag.dim, facet_tag.find(1))
bcs = [fem.dirichletbc(u_bc, left_dofs, V)]
Next, we define the body force on the reference configuration (B), and nominal (first Piola-Kirchhoff) traction (T).
B = fem.Constant(domain, default_scalar_type((0, 0, 0)))
T = fem.Constant(domain, default_scalar_type((0, 0, 0)))
Define the test and solution functions on the space \(V\)
v = ufl.TestFunction(V)
u = fem.Function(V)
Define kinematic quantities used in the problem
# Spatial dimension
d = len(u)
# Identity tensor
I = ufl.variable(ufl.Identity(d))
# Deformation gradient
F = ufl.variable(I + ufl.grad(u))
# Right Cauchy-Green tensor
C = ufl.variable(F.T * F)
# Invariants of deformation tensors
Ic = ufl.variable(ufl.tr(C))
J = ufl.variable(ufl.det(F))
Define the elasticity model via a stored strain energy density function \(\psi\), and create the expression for the first Piola-Kirchhoff stress:
Elasticity parameters
E = default_scalar_type(1.0e4)
nu = default_scalar_type(0.3)
mu = fem.Constant(domain, E / (2 * (1 + nu)))
lmbda = fem.Constant(domain, E * nu / ((1 + nu) * (1 - 2 * nu)))
Stored strain energy density (compressible neo-Hookean model)
Hyper-elasticity
P = ufl.diff(psi, F)
Comparison to linear elasticity
To illustrate the difference between linear and hyperelasticity, the following lines can be uncommented to solve the linear elasticity problem.
# P = 2.0 * mu * ufl.sym(ufl.grad(u)) + lmbda * ufl.tr(ufl.sym(ufl.grad(u))) * I
Define the variational form with traction integral over all facets with value 2. We set the quadrature degree for the integrals to 4.
metadata = {"quadrature_degree": 4}
ds = ufl.Measure("ds", domain=domain, subdomain_data=facet_tag, metadata=metadata)
dx = ufl.Measure("dx", domain=domain, metadata=metadata)
Define the residual of the equation (we want to find u such that residual(u) = 0)
As the varitional form is non-linear and written on residual form, we use the non-linear problem class from DOLFINx to set up required structures to use a Newton solver.
petsc_options = {
"snes_type": "newtonls",
"snes_linesearch_type": "none",
"snes_monitor": None,
"snes_atol": 1e-8,
"snes_rtol": 1e-8,
"snes_stol": 1e-8,
"ksp_type": "preonly",
"pc_type": "lu",
"pc_factor_mat_solver_type": "mumps",
}
problem = NonlinearProblem(
residual,
u,
bcs=bcs,
petsc_options=petsc_options,
petsc_options_prefix="hyperelasticity",
)
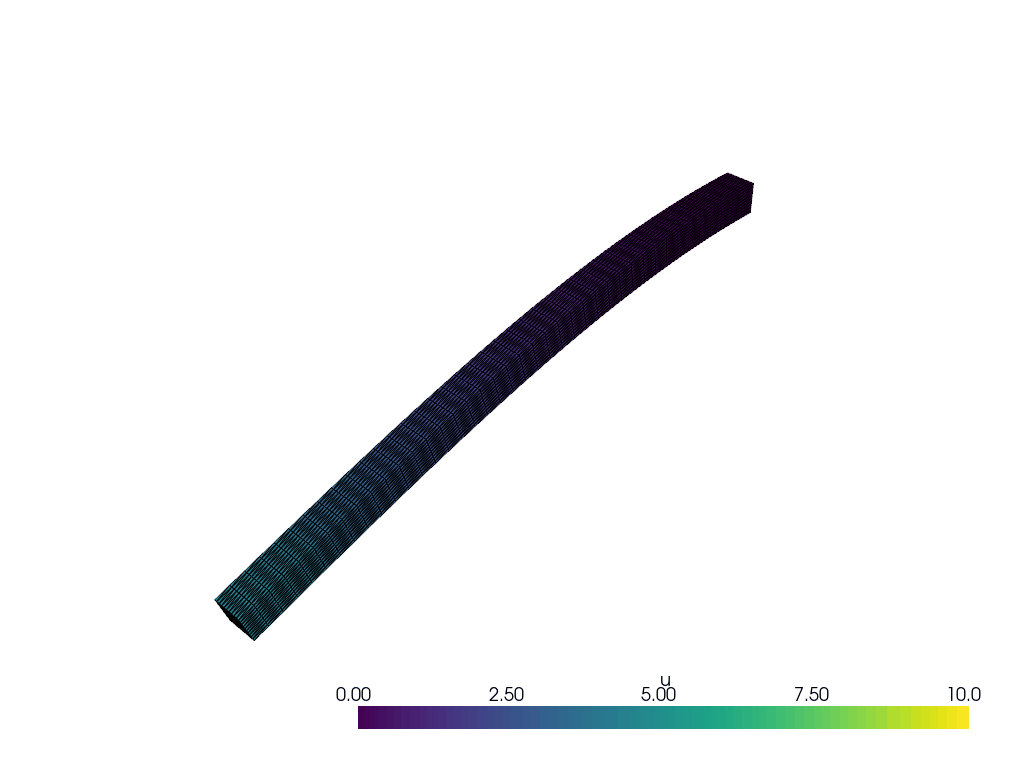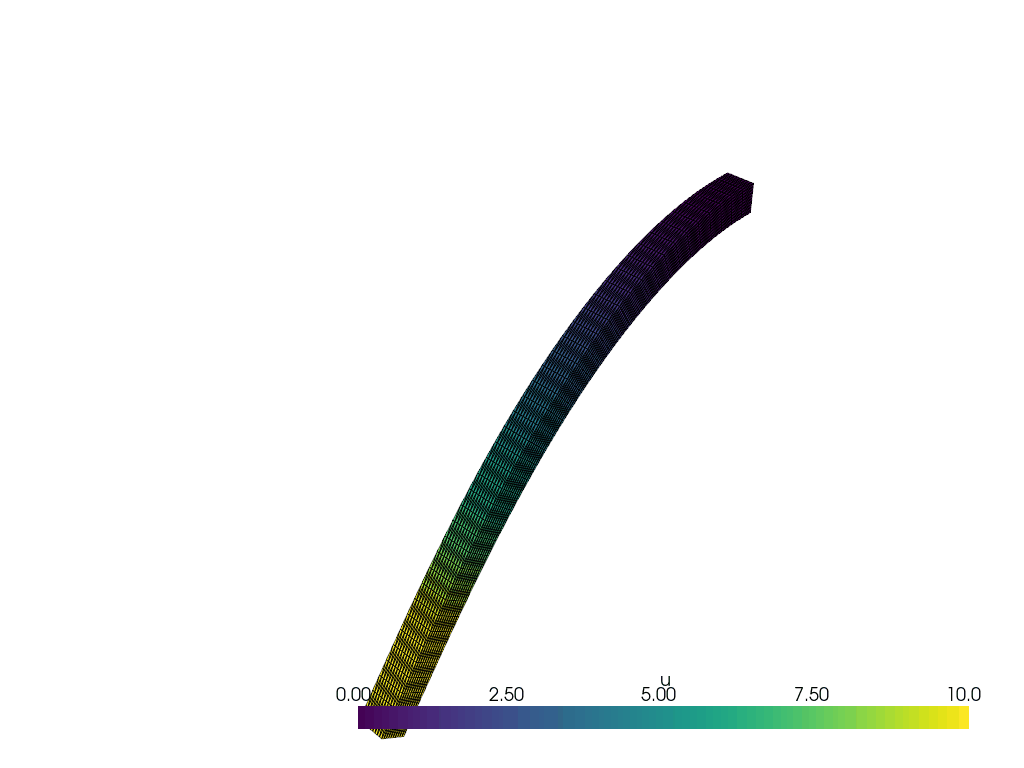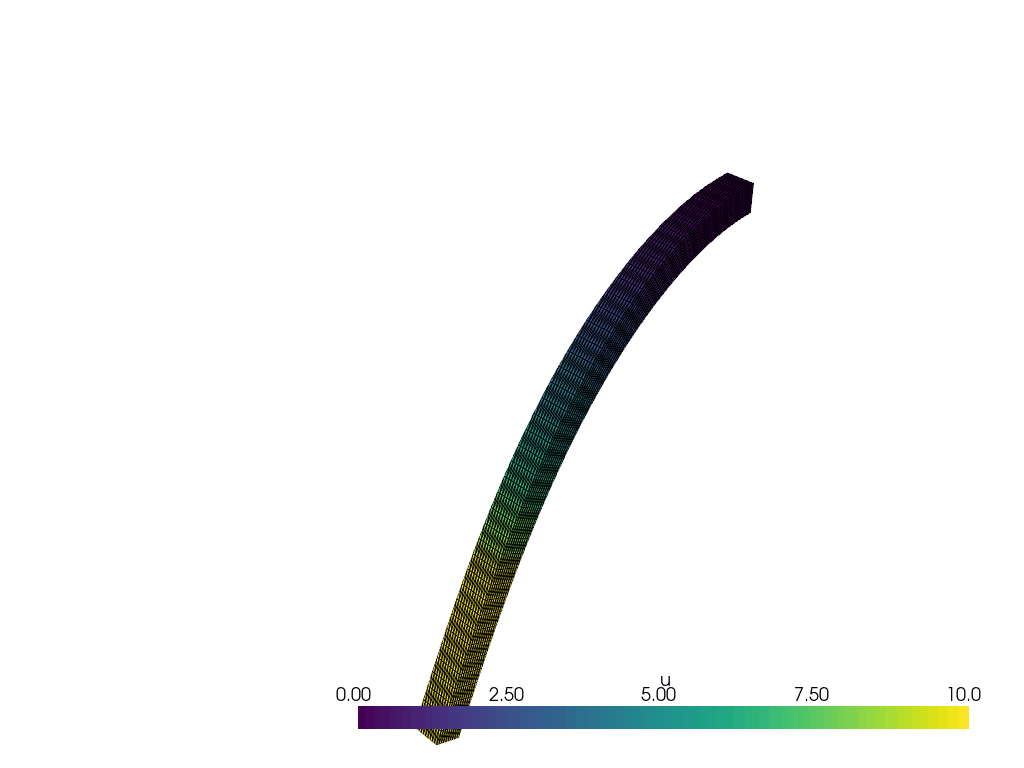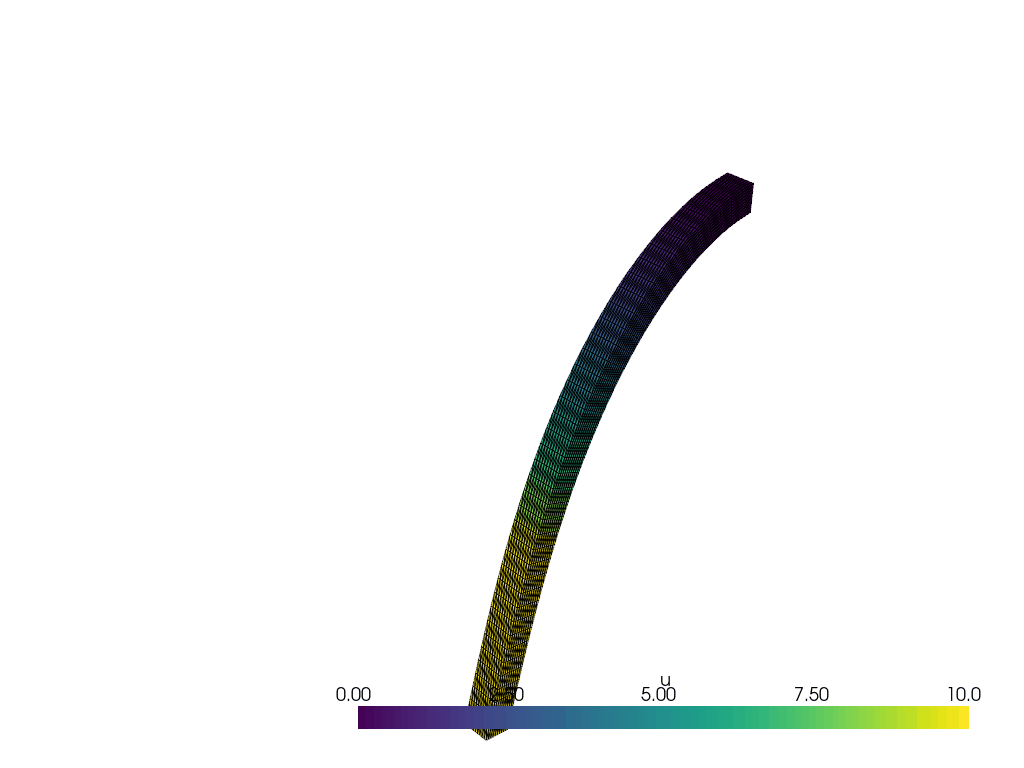
We create a function to plot the solution at each time step.
plotter = pyvista.Plotter()
plotter.open_gif("deformation.gif", fps=3)
topology, cells, geometry = plot.vtk_mesh(u.function_space)
function_grid = pyvista.UnstructuredGrid(topology, cells, geometry)
values = np.zeros((geometry.shape[0], 3))
values[:, : len(u)] = u.x.array.reshape(geometry.shape[0], len(u))
function_grid["u"] = values
function_grid.set_active_vectors("u")
# Warp mesh by deformation
warped = function_grid.warp_by_vector("u", factor=1)
warped.set_active_vectors("u")
# Add mesh to plotter and visualize
actor = plotter.add_mesh(warped, show_edges=True, lighting=False, clim=[0, 10])
# Compute magnitude of displacement to visualize in GIF
Vs = fem.functionspace(domain, ("Lagrange", 2))
magnitude = fem.Function(Vs)
us = fem.Expression(
ufl.sqrt(sum([u[i] ** 2 for i in range(len(u))])), Vs.element.interpolation_points
)
magnitude.interpolate(us)
warped["mag"] = magnitude.x.array
2026-03-02 08:11:02.299 ( 2.773s) [ 7F86A186F140]vtkXOpenGLRenderWindow.:1458 WARN| bad X server connection. DISPLAY=
Finally, we solve the problem over several time steps, updating the z-component of the traction
log.set_log_level(log.LogLevel.INFO)
tval0 = -1.5
for n in range(1, 10):
T.value[2] = n * tval0
problem.solve()
converged = problem.solver.getConvergedReason() > 0
num_its = problem.solver.getIterationNumber()
assert converged > 0, f"Solver did not converge with reason {converged}."
print(f"Time step {n}, Number of iterations {num_its}, Load {T.value}")
function_grid["u"][:, : len(u)] = u.x.array.reshape(geometry.shape[0], len(u))
magnitude.interpolate(us)
warped.set_active_scalars("mag")
warped_n = function_grid.warp_by_vector(factor=1)
warped.points[:, :] = warped_n.points
warped.point_data["mag"][:] = magnitude.x.array
plotter.update_scalar_bar_range([0, 10])
plotter.write_frame()
plotter.close()
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333333333e-01
1 SNES Function norm 1.330753374744e+03
2 SNES Function norm 7.390366918218e+01
3 SNES Function norm 4.714331088814e-01
4 SNES Function norm 9.045604878146e-01
5 SNES Function norm 1.011600107993e-03
6 SNES Function norm 2.328092279469e-05
7 SNES Function norm 1.880942653761e-10
Time step 1, Number of iterations 7, Load [ 0. 0. -1.5]
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333333349e-01
1 SNES Function norm 1.053155719085e+03
2 SNES Function norm 4.497738442463e+01
3 SNES Function norm 1.597191934430e+00
4 SNES Function norm 1.008829276538e+01
5 SNES Function norm 3.363230678630e-02
6 SNES Function norm 1.161567324497e-01
7 SNES Function norm 4.338360833840e-06
8 SNES Function norm 2.483425680583e-09
Time step 2, Number of iterations 8, Load [ 0. 0. -3.]
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333331859e-01
1 SNES Function norm 6.157586973064e+02
2 SNES Function norm 1.460711281346e+01
3 SNES Function norm 3.318947789756e+00
4 SNES Function norm 1.009685403909e+01
5 SNES Function norm 4.185327720876e-01
6 SNES Function norm 1.058465189904e+00
7 SNES Function norm 3.889935993309e-03
8 SNES Function norm 1.252948744246e-04
9 SNES Function norm 3.750009972458e-10
Time step 3, Number of iterations 9, Load [ 0. 0. -4.5]
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333333265e-01
1 SNES Function norm 3.351285836746e+02
2 SNES Function norm 4.135214434652e+00
3 SNES Function norm 4.493073600804e+01
4 SNES Function norm 3.405823774840e-01
5 SNES Function norm 1.363506146250e+01
6 SNES Function norm 7.670312540678e-03
7 SNES Function norm 5.774813085169e-03
8 SNES Function norm 7.143776264740e-09
Time step 4, Number of iterations 8, Load [ 0. 0. -6.]
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333325048e-01
1 SNES Function norm 1.880704733464e+02
2 SNES Function norm 1.252286183190e+00
3 SNES Function norm 3.609070573922e+00
4 SNES Function norm 4.953401651173e-02
5 SNES Function norm 9.623194860043e-03
6 SNES Function norm 3.341820656077e-07
7 SNES Function norm 4.383107694299e-10
Time step 5, Number of iterations 7, Load [ 0. 0. -7.5]
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333333365e-01
1 SNES Function norm 1.116094096457e+02
2 SNES Function norm 4.247396798122e-01
3 SNES Function norm 1.262748206071e+00
4 SNES Function norm 2.317735911326e-03
5 SNES Function norm 4.305377182770e-05
6 SNES Function norm 4.497644754916e-10
Time step 6, Number of iterations 6, Load [ 0. 0. -9.]
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333333317e-01
1 SNES Function norm 7.005111548270e+01
2 SNES Function norm 1.606542965112e-01
3 SNES Function norm 5.406329894063e-01
4 SNES Function norm 1.096042518976e-04
5 SNES Function norm 2.999948245372e-07
6 SNES Function norm 4.485076259009e-10
Time step 7, Number of iterations 6, Load [ 0. 0. -10.5]
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333333356e-01
1 SNES Function norm 4.622497140491e+01
2 SNES Function norm 6.753406526318e-02
3 SNES Function norm 2.415083570394e-01
4 SNES Function norm 4.656934898605e-06
5 SNES Function norm 2.054196725700e-09
Time step 8, Number of iterations 5, Load [ 0. 0. -12.]
0 SNES Function norm 1.633333331306e-01
1 SNES Function norm 3.185930870265e+01
2 SNES Function norm 3.414437567892e-02
3 SNES Function norm 1.076837937757e-01
4 SNES Function norm 4.272634938671e-07
5 SNES Function norm 4.849589787623e-10
Time step 9, Number of iterations 5, Load [ 0. 0. -13.5]